In this article, we’ll explore the working principles, basic components, operational procedures, and maintenance of the Sunrui Ballast Water Management System (BalClor® BWMS). Let’s dive in!
1. Working Principles of BalClor® BWMS
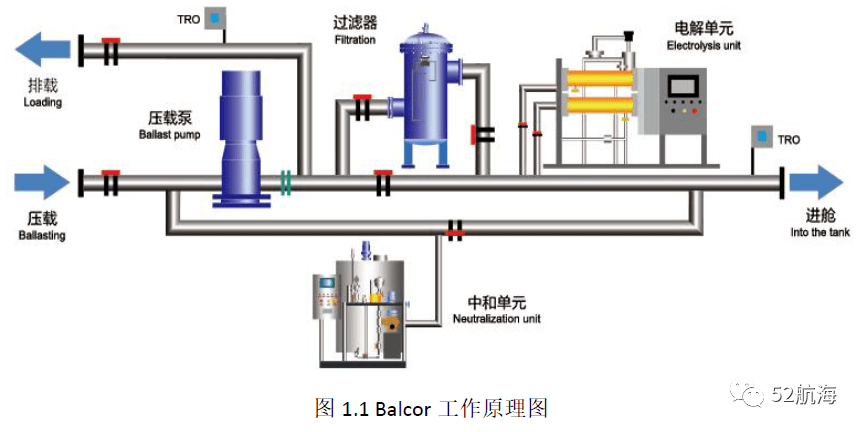
The BalClor® BWMS treats ballast water through three main steps: filtration, electrolysis to produce sodium hypochlorite for disinfection, and neutralization.
- Filtration: During ballasting, all ballast water passes through an automatic backwash filter with a precision of 50 microns. This step removes most marine organisms and solid particles larger than 50 microns.
- Electrolysis for Disinfection: A small flow of seawater is diverted from the ballast water main line to an electrolysis unit. Here, electrolysis generates a high concentration of sodium hypochlorite solution, which is then injected back into the ballast water main line after degassing. This solution effectively kills residual plankton, pathogens, larvae, or spores, meeting required sterilization standards.
- Neutralization: During deballasting, a neutralization system is activated to inject neutralizing agents into the discharge pipe, neutralizing any remaining oxidants.
2. Basic Components of BalClor® BWMS
- Electrolysis Unit (EDU): Generates sodium hypochlorite solution through electrolysis of seawater and injects it into the ballast main line.
- Automatic Backwash Filter (AFU): Filters ballast water during ballasting, removing particles larger than 50 microns. It automatically initiates backwashing when the pressure difference reaches a certain value.
- Neutralization Unit (ANU): Injects neutralizing agents into the discharge pipe to neutralize any remaining oxidants.
- Residual Chlorine Analyzer (TRO): Monitors chlorine ion levels in the ballast water during electrolysis and discharge processes.
- Control Cabinet and Rectifier: Controls and regulates the operation of the system.
