The Techcross ballast water treatment system uses electrolysis to produce active substances that kill microorganisms in ballast water. It consists of several key units, including CPC, PDE, PRU, TSU, ANU, and FMU. Below, we explain the main units and how to troubleshoot common issues.
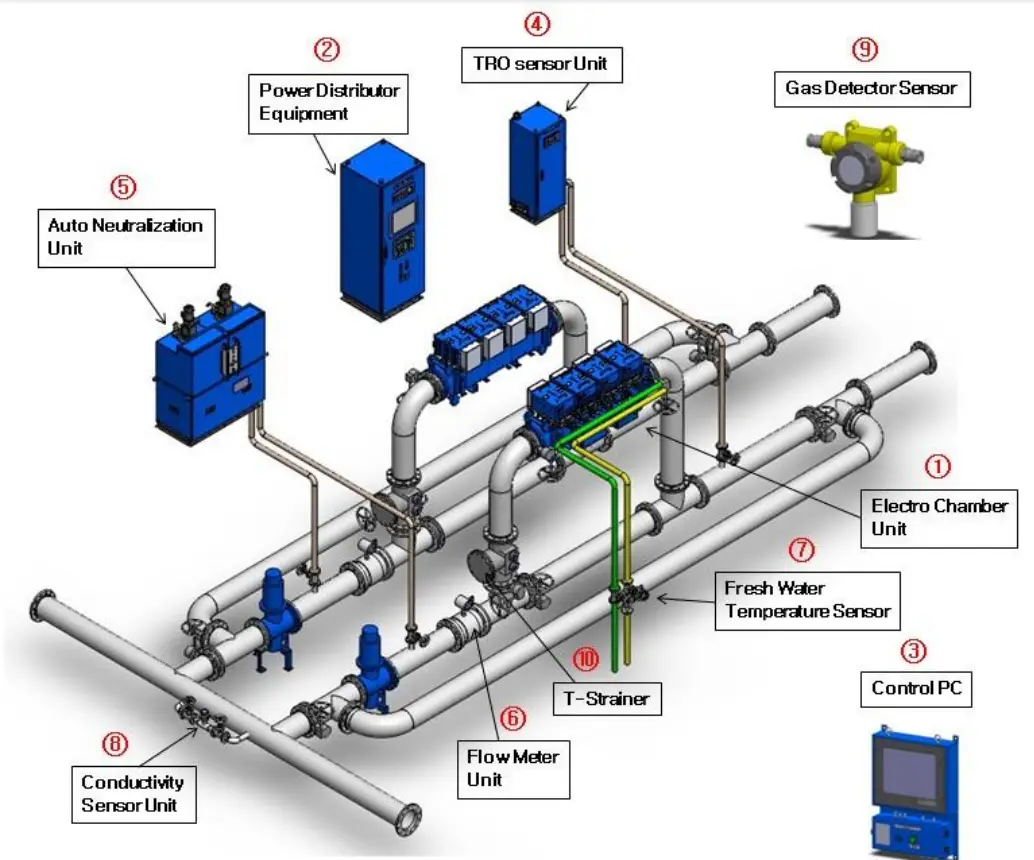
How It Works
1. CPC (Control Panel Computer)
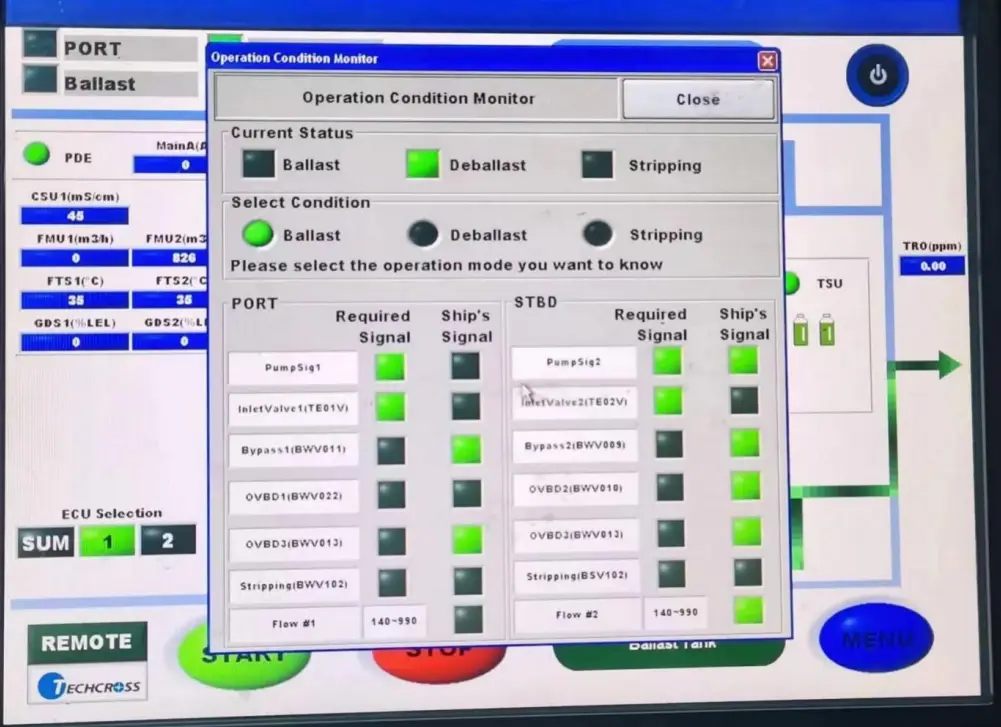
- The CPC is the user interface with two computers: one in the ballast water operation room and one in the engine room.
- It allows operators to control ballast water operations and provides information about the status of valves, pumps, and system parameters.
- The left side shows required signals for ballast water operations. Operators must open the corresponding valves to ensure the right signals are met for the system to start.
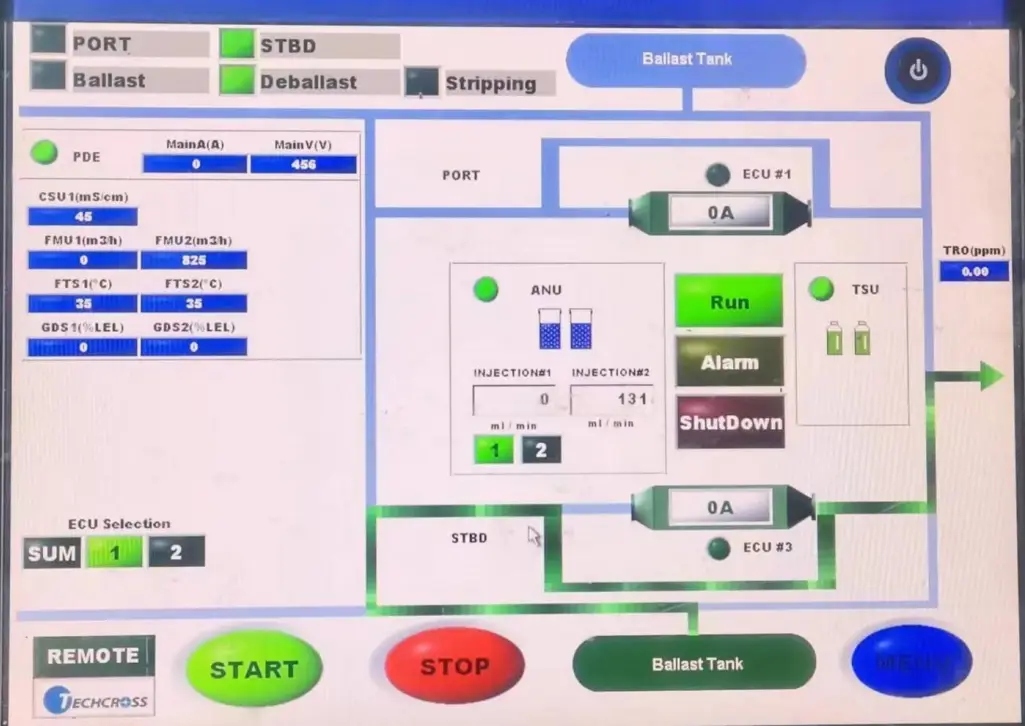
2. PDE (Power Distribution Unit)
- The PDE supplies 440V AC power to all system components and manages communication between control units.
3. Electrolysis Units
- The electrolysis process occurs in units like the ECU signal junction box (ESJ), ECU power junction box (EPJ), power rectifier unit (PRU), and electric chamber unit.
- The PRU provides a current of less than 1125A for electrolysis to generate active substances. Each system has six electrolysis units with independent freshwater cooling systems.
- It’s crucial to monitor the current during operations. High currents can damage the system, so operators should regularly check the cooling water temperature and ensure proper cooling.
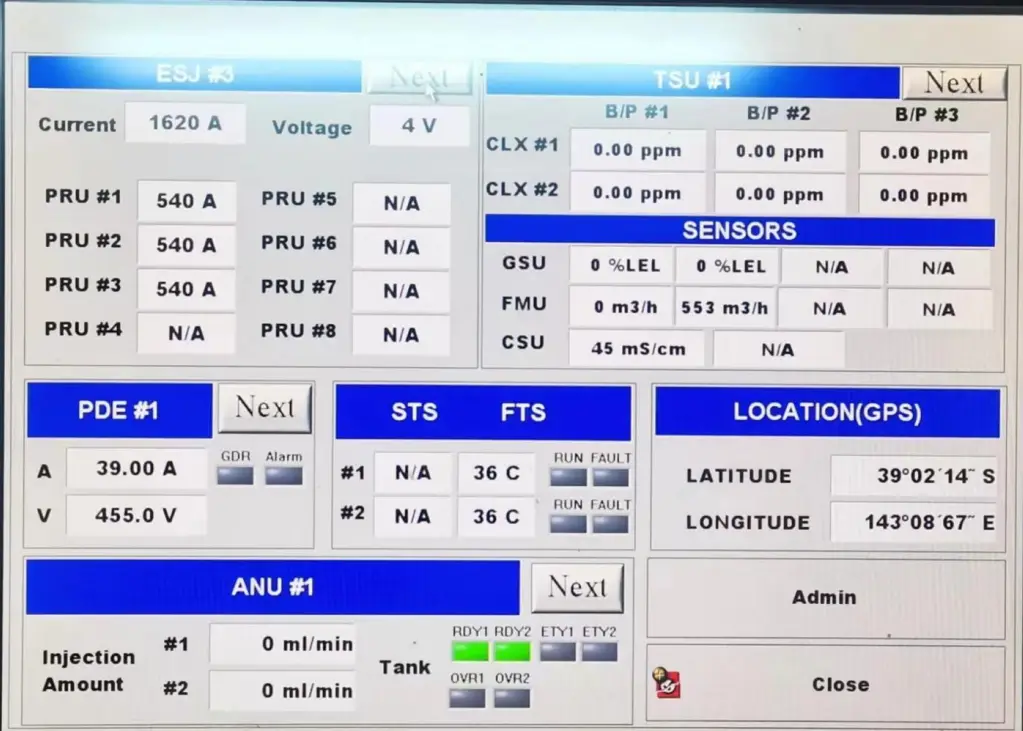
4. TSU (Treatment Sampling Unit)
- The TSU samples ballast water to check residual oxidant levels using an air pump.
- During ballasting, the Target Residual Oxidant (TRO) should be between 5-10 ppm; during discharge, it should be below 0.2 ppm.
- The chemical reagents in the TSU should be replaced every two months.
5. ANU (Active Neutralization Unit)
- The ANU controls the injection of sodium thiosulfate solution to reduce the TRO during discharge operations.
- Typically, there are two ANU units, each with two dosing pumps.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Low TRO Value
- Causes include insufficient electrolysis or issues with the TSU.
- Check if the ECU units are functioning and monitor the system’s current. Regular cleaning and maintenance are necessary.
2. High TRO Value
- This issue often arises during discharge if the ANU is not working correctly.
- Verify the concentration of sodium thiosulfate and check the injection system for blockages or failures.


3. Low Flow Rate During Ballasting
- A common cause is a clogged T-type filter from dirty port water.
- Cleaning the filter can restore normal flow.
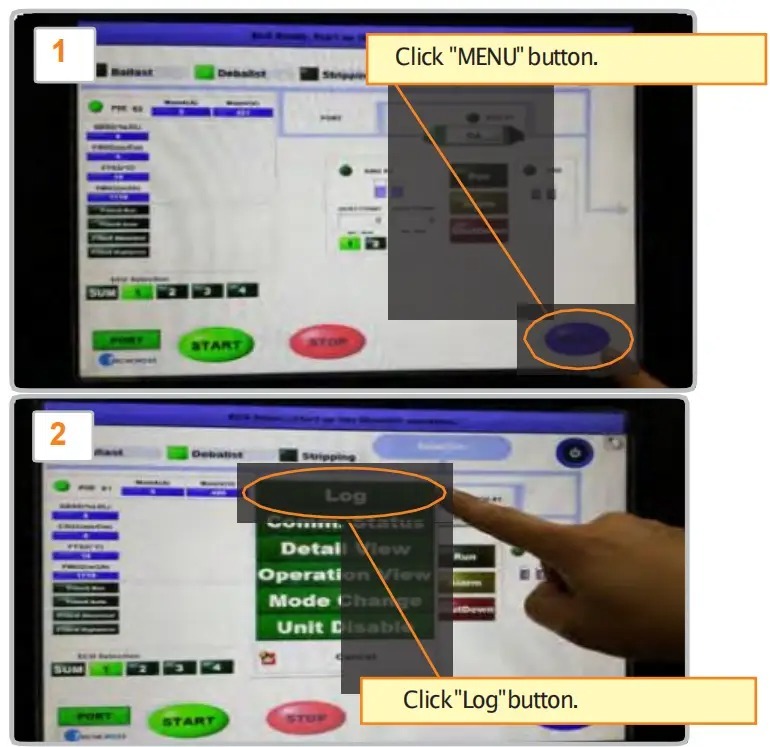

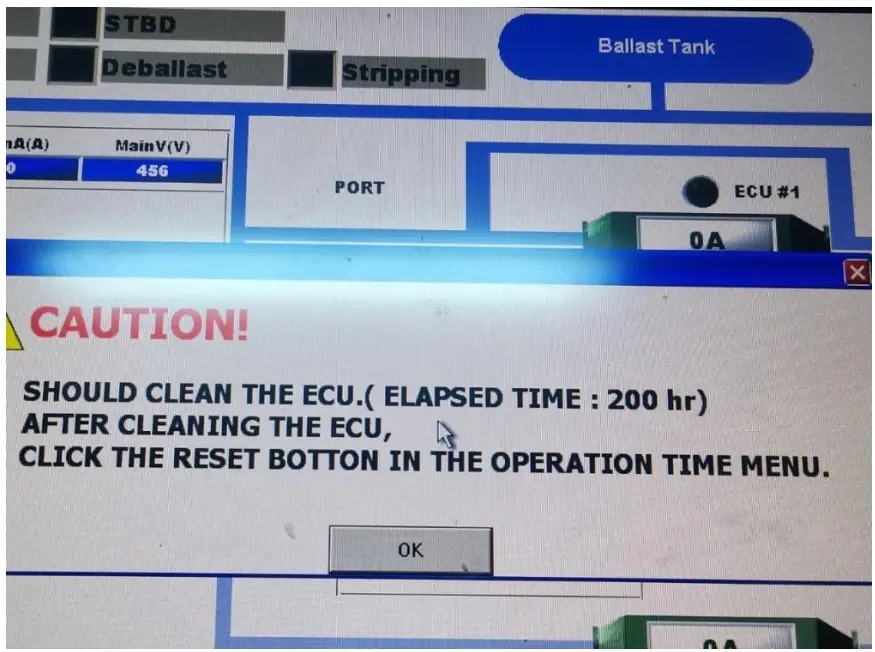
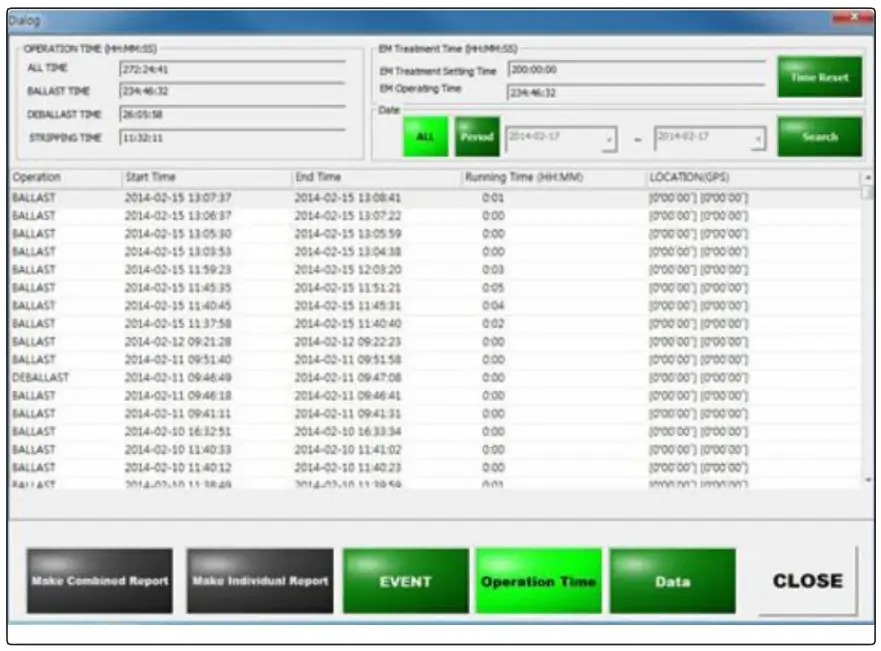
Generating Reports
- The system records ballast operations, which can be generated as PDF documents via the CPC interface.
- Regularly back up reports to avoid storage issues.
